Introduction
Have you ever tried to install a new operating system or upgrade your storage drive, only to be met with an error about “MBR limitations” or “UEFI requirements”? If so, you’re not alone. As data storage demands grow, older partitioning schemes like the Master Boot Record (MBR) struggle to keep up. Enter the GUID Partition Table (GPT)—a modern solution that overcomes MBR’s limitations and is the preferred partitioning scheme for today’s high-capacity drives.
In this article, we’ll explore what the GUID Partition Table (GPT) is, how it differs from MBR, and why it is essential for modern computing. Whether you’re an IT professional, network administrator, DevOps engineer, or cybersecurity specialist, understanding GPT will help you manage storage devices more effectively and ensure system compatibility with the latest hardware.
Quick Answer: What is GUID Partition Table (GPT)?
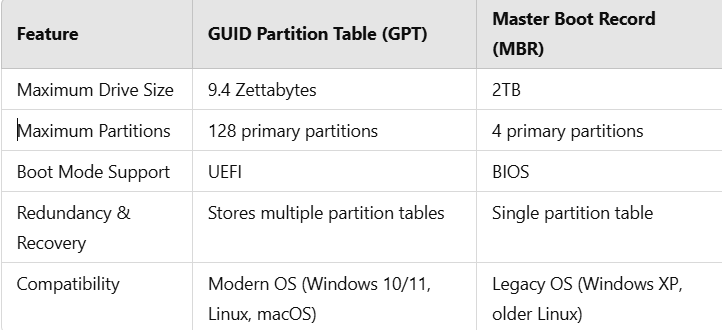
The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a modern partitioning scheme that replaces the Master Boot Record (MBR). Unlike MBR, GPT supports larger disk sizes (beyond 2TB), stores multiple copies of partition data for reliability, and works with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) instead of legacy BIOS.
Key Takeaways:
- Supports larger drives: GPT can handle storage devices beyond 2TB, unlike MBR, which is limited to 2TB.
- Improved reliability: GPT stores multiple copies of partition data, reducing the risk of partition corruption.
- Required for UEFI boot mode: Modern operating systems and UEFI firmware require GPT instead of MBR.
- Allows more partitions: GPT supports up to 128 primary partitions, whereas MBR is limited to only 4.
- Future-proof technology: With storage needs increasing, GPT is the preferred standard for modern computing.
GPT vs. MBR: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding GPT Structure
A GPT-based disk consists of the following key components:
1. Protective MBR
Even though GPT replaces MBR, it still includes a small protective MBR for backward compatibility with older tools that might not recognize GPT.
2. Primary GPT Header
This contains critical information about the disk layout, including:
- Disk GUID (Globally Unique Identifier)
- Partition table location
- Partition entries
3. Partition Entries
Each partition is assigned a unique GUID, making it easy for the system to identify and manage them.
4. Secondary GPT Header
To improve reliability, a backup GPT header is stored at the end of the disk.
When Should You Use GPT?
- When using high-capacity drives (above 2TB)
- If your system uses UEFI instead of BIOS
- When creating more than four partitions on a disk
- For enterprise servers and cloud environments requiring data integrity
Did You Know?
👉 GPT disks use CRC32 checksums to detect and recover from partition table corruption, making them far more reliable than MBR disks!
How to Convert MBR to GPT
If you have an existing MBR disk and need to convert it to GPT, here’s how:
Method 1: Using Disk Management (Windows)
- Open Disk Management (
diskmgmt.msc). - Right-click the target disk and select Convert to GPT Disk.
- Note: This method requires deleting all partitions, so backup your data first!
Method 2: Using Command Line (diskpart)
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type:

Method 3: Using Third-Party Tools (Non-Destructive)
- Tools like EaseUS Partition Master and Minitool Partition Wizard allow conversion without deleting data.
Important Note ⚠️
Converting an MBR disk to GPT erases all data unless you use third-party tools that support non-destructive conversion. Always backup critical files before proceeding!
GPT and UEFI: The Perfect Pair
For modern hardware, UEFI and GPT work hand in hand. UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) replaces legacy BIOS and offers features such as:
- Faster boot times
- Secure Boot support
- Native support for large storage devices
To check if your system supports UEFI:
- Open System Information (
msinfo32in Windows Run command). - Look for BIOS Mode:
- If it says UEFI, you can use GPT.
- If it says Legacy, your system is using BIOS.
FAQs About GPT
Q1: Can GPT work with BIOS?
No, GPT requires UEFI for booting. However, data storage GPT disks work fine on BIOS systems.
Q2: Is GPT compatible with all operating systems?
- Windows 10/11, Linux, macOS: Fully supports GPT.
- Windows 7 (64-bit): Limited support.
- Older Windows (XP, 7 32-bit): No support.
Q3: Should I use GPT or MBR for SSDs?
Always use GPT for SSDs, as it offers better performance and reliability.
Conclusion
The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is the future of partitioning, offering greater storage capacity, reliability, and flexibility compared to the older MBR format. Whether you’re upgrading your system, managing cloud storage, or configuring enterprise servers, understanding and using GPT will ensure better performance and long-term compatibility.
🔹 Need help converting your disk to GPT? Start with built-in tools like Disk Management or diskpart, or opt for third-party utilities for a safer conversion.
📢 Have you faced issues with GPT vs. MBR? Share your experience in the comments below!

This article was both educational and enjoyable to read.
The site offers a lot of similar high-quality content, which I love.